Initial experience using contrast enhanced real-time three-dimensional exercise stress echocardiography in a low-risk population
Abstract
Overview
Although emerging data support the utility
of real-time three-dimensional echocardiography
(RT3DE) during dobutamine stress testing,
the feasibility of performing contrast
enhanced RT3DE during exercise treadmill
stress has not been explored. Two-dimensional
(2D) and three-dimensional (3D) acquisition
were performed in 39 patients at rest and
peak exercise. Contrast was used in 29
patients (74%). Reconstruction was performed
manually by generating short axis cut
planes at the base, mid-ventricle and apex,
and automatically by generating 9 short axis
slices. Three-dimensional acquisition was feasible
during rest and stress regardless of the
use of contrast. Time to acquire stress images
was reduced using 3D (35.2±17.9 s) as compared
to 2D acquisition (51.6±14.7 s; P<0.05). Using a 17-segment model, of all 663 segments,
588 resting (88.6%) and 563 stress segments
(84.9%) were adequately visualized
using manually reconstructed 3D data, compared
with 618 resting (93.2%) and 606 stress
segments (91.4%) using 2D data (P rest=0.06;
P stress=0.07). We concluded that contrast
enhanced RT3DE is feasible during treadmill
stress echocardiography.
Keywords
Three-dimensional exercise stress echocardiography.
Article Information
Correspondence
Smadar Kort, Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, HSC T-16 080, Stony Brook University Medical Center, Stony Brook, NY 11974-8167, USA. E-mail: smadar.kort@stonybrook.edu
Received
2010-03-01T00:00:00
Further Resources

Trending Topic
As of the publication of this article, the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection has affected over 400 million people around the world and caused over 6 million deaths.1 Although COVID-19 infection predominantly affects the respiratory system, studies have described a wide spectrum of cardiovascular manifestations, including asymptomatic myocardial injury, myocardial infarction and myocarditis.2 Echocardiography is an easily […]
Related Content in Imaging

More than half of acute coronary syndromes (ACS) occur in subjects with no significant coronary stenosis.1 In view of the number of patients dying each year from a heart attack, the question of identifying these patients is of primary importance. ...

Left main Stenosis Stenting Normalizes Wall Shear Stress of Ascending Aorta in Bicuspid Aortic Valve
Bicuspid aortic valve (BAV) represents the most common congenital cardiac anomaly, with a prevalence ranging between 1% and 2% in the general population.1 BAV is known to be associated with dilation and dissection of the ascending aorta, and the significantly higher shear ...

Anomalous coronary arteries originating from the opposite sinus of Valsalva (ACAOS) is one of the most clinically relevant abnormalities among the wide spectrum of coronary artery anomalies.1 Sudden cardiac death has been related to myocardial bridges, ectopic origin of the ...

Introduction: The restriction of activation mapping to the ventricular surface of contemporary mapping systems often leads to failure to correctly identify the true site of origin (SOO) of intramural and/or sub-epicardial Vas and lower procedural success. Electromechanical wave imaging (...

Introduction: Leadless left ventricular (LV) endocardial pacing with the WiSE-CRT System (EBR Systems Inc) is a novel treatment in the field of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). The system was designed to provide lateral wall LV pacing (LVP) in response to ...

Background: The spatial resolution of a mapping catheter is determined by factors such as the quantity of electrodes, their inter-electrode spacing, and the various configurations in which they are utilized. These factors impact the interpretation of wavefront dynamics during cardiac ...

Background: Obesity-related cardiac remodelling may be reflected through electrocardiogram (ECG) changes. Based on this premise, we hypothesised that an artificial intelligence (AI)-ECG model could be trained to predict body mass index (BMI), and that the difference between AI-ECG predicted ...

Athletes represent the fittest individuals in our society, yet paradoxically carry an increased risk of sudden cardiac death (SCD) when compared to sedentary individuals with the same cardiac disease.1,2 Two recent studies have provided a realistic prevalence of young SCD ...

Sudden cardiac death arises from the unexpected stopping of the heart and is associated with up to a half of cardiovascular deaths. We discuss with Professor Martin Borggrefe how to identify patient populations at risk of sudden cardiac death (...
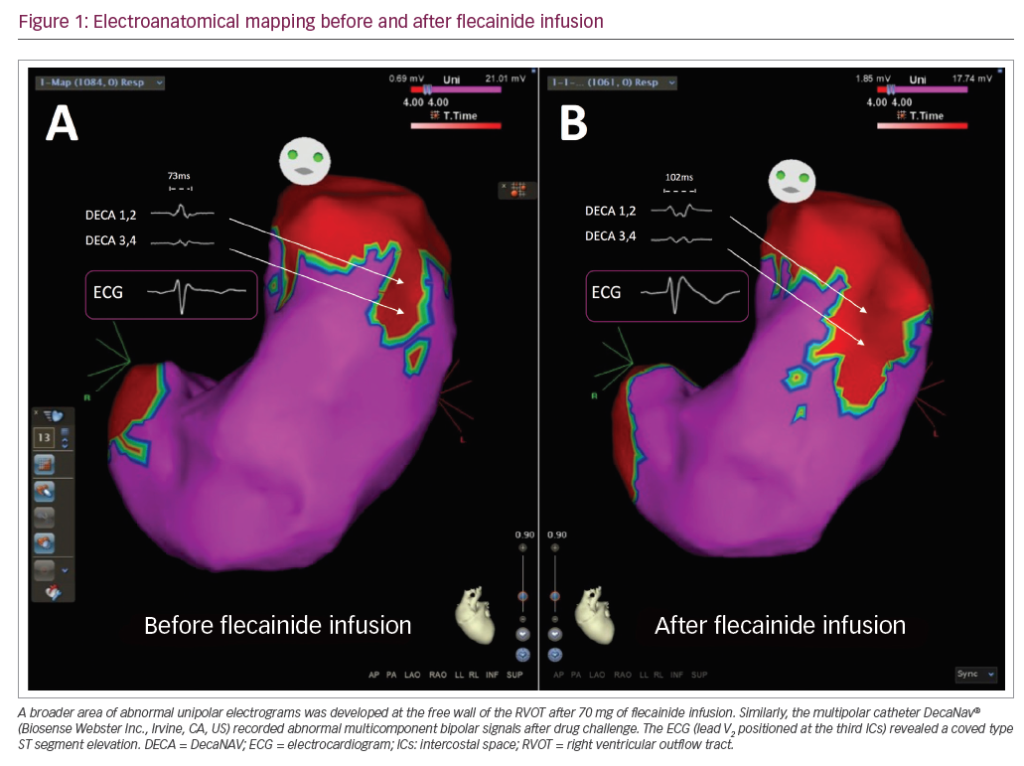
Brugada syndrome (BrS) is a genetic arrhythmia syndrome with increased risk of sudden cardiac death. Unmasking a type I BrS electrocardiogram (ECG) pattern after administration of sodium channel blockers may be associated with an increase in epicardial substrate abnormalities. We ...
Latest articles videos and clinical updates - straight to your inbox
Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Register now for FREE Access
Register for free to hear about the latest expert-led education, peer-reviewed articles, conference highlights, and innovative CME activities.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a Social Account.
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.

