Antiplatelet agents are routinely given to prevent thrombosis of coronary stents.1 When antiplatelet drugs are not given before percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), they may be given on the table during PCI.1 Ingestion of pills while supine on the catheterisation table often causes mild dysphagia and discomfort but, rarely, it can cause a more serious event. We report a case of pill oesophagitis following supine clopidogrel tablet ingestion, likely due to clopidogrel lodging in the oesophagus during a coronary stenting procedure.
Case history
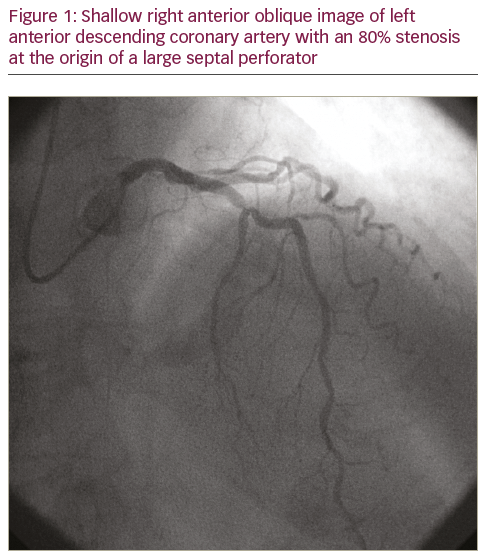
A 78-year-old female presented for elective cardiac catheterisation for class II angina. She was symptomatic despite using isosorbide mononitrate 30 mg daily and metoprolol tartrate 50 mg twice daily. Cardiac catheterisation showed 80% stenosis in the mid-left anterior descending coronary artery (Figure 1). Ad hoc PCI with a drug-eluting stent (2.5 x 12.0 mm Xience V® stent, Abbott Vascular, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was performed (Figure 2). Clopidogrel (six 75 mg tablets) was administered on the table after diagnostic imaging and before PCI. After PCI the patient reported discomfort deep in her throat, which started when clopidogrel was ingested and persisted for several hours. This discomfort was separate to her baseline angina and the electrocardiogram was normal, so her symptoms were attributed to difficulty swallowing the clopidogrel tablets. Her discomfort resolved and she was discharged later the same day in a good condition.

Routine telephone follow-up was conducted the next day. The patient reported that she had solid-food dysphagia and non-exertional chest discomfort, which was different compared with her previous angina. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy 1 day later showed two ulcers with no evidence of luminal narrowing or stricture in the middle third of the oesophagus (Figure 3A–D), consistent with pill oesophagitis. She was treated with omeprazole 20 mg twice daily and sucralfate suspension 1 g, by mouth, four times a day, for 8 weeks. Her symptoms resolved over the next few days and repeat endoscopy 8 weeks later showed healing of the oesophageal ulcers (Figure 3E).

Discussion
We believe this is the first reported case of pill oesophagitis attributable to a thienopyridine drug, or any drug given during PCI. We attribute the patient’s oesophagitis to ingestion of 6 clopidogrel tablets while lying supine on the catheterisation laboratory table and hypothesise that at least one tablet lodged in her mid-oesophagitis. This is supported by the fact that she noticed discomfort deep in her throat that persisted several hours after ingesting the clopidogrel tablets. The linear ulcerations found on endoscopy were felt by the endoscopist to be typical of pill oesophagitis.
Other possible causes of her oesophagitis seem less likely. She was taking aspirin 81 mg daily but reported no oesophageal symptoms on visits over several years prior to catheterisation. She received 324 mg of aspirin on the morning of catheterisation, sitting upright and taken with water, but had no trouble ingesting this. Endoscopy 8 weeks later showed complete resolution of oesophagitis despite continuing aspirin 81 mg per day and clopidogrel 75 mg per day. On subsequent visits to her cardiology and pulmonary physicians, she reported no further chest pains or oesophageal symptoms. However, despite these points, we cannot completely exclude other causes.
Difficulty ingesting pills is very common,2 and can lead to pills lodging in the oesophagus, which has been reported with doxycycline, anti-inflammatory drugs, potassium chloride and bisphosphonates.3,4 It is usually self-limited but, rarely, it can lead to haemorrhage, stricture, perforation and mediastinitis.4 The characteristics of the culprit medication can predispose to oesophageal injury, including its chemical
constitution, the size and the coatings of the pill and contact time with the mucosa, which can be influenced by oesophageal motility abnormality, left atrial enlargement, recumbent position and inadequate amounts of fluid.4 While proton-pump inhibitors do not prevent oesophageal erosions associated with antiplatelet agents,5 they are commonly used to treat pill oesophagitis.6
Pill oesophagitis might be responsible for some of the upper gastrointestinal discomfort7 or pill intolerance8 that affect clopidogrel adherence. If the pill remains in the oesophagus for a prolonged interval
or absorption is incomplete, this might delay the achievement of therapeutic serum levels of the medication, and increase the risk of stent thrombosis. Patients undergoing elective PCI are often discharged on the day of the procedure, and symptoms of pill oesophagitis may develop only after discharge and be reported to their primary care physicians, who may not be aware of the risk of this entity. Finally, symptoms of pill oesophagitis may be easily confused with recurrent angina or ischaemia after PCI, so awareness of this entity may help physicians avoid referral for unneeded hospitalisations or repeat catheterisations.
Ideally, patients would be loaded with P2Y12 receptor inhibitors before undergoing diagnostic procedures that lead to PCI. However, since pre-loading may delay bypass surgery if severe multi-vessel disease is identified, often pre-loading is not performed and patients are given antiplatelet drugs on the table. In these cases, adequate ingestion should be ensured. It is prudent to ask about oesophageal motility disorders or symptoms of dysphagia before asking patients to ingest medications when supine. Adequate water should
be given to flush the medications through the oesophagus. It may be possible to raise the patient’s head and torso slightly off the table to aid swallowing, particularly if radial access is used, since an upright position decreases the risk of medications lodging in the oesophagus.3